Before microservices, the load balancing solution was mainly a centralized load balancer. There was another independent load balancer between service consumers and service providers. Load balancer is usually specialized hardware, such as F5, or software-based, such as VS, HAproxy. There is an address mapping table for all services on the load balancer. When a service consumer invokes a target service, it initiates a request to the load balancer, and the load balancer forwards the request to the target server after performing load balancing using a certain strategy (such as Round-Robin).
The emergence of microservices provides another idea for the implementation of load balancer: encapsulate the functions of load balancing into a library and integrate it with the service consumer’s process, rather than provide a centralized device or server. This solution is called Soft Load Balancing or Client Load Balancing. In conjunction with the service discovery function of Eureka in Spring Cloud, the Ribbon sub-project implements load balancing for REST clients.
Example Project
1. We can extend the eureka demo project
Code: Eureka demo
2. Add Dependency to service-hello-consumer
1 | <dependency> |
3. Main Class
1 |
|
In this main class:
@EnableDiscoveryClientannotation, indicating that this is anEurekaclient, and can also get a list of services registered in theEureka server;- We have added a
@LoadBalancedannotation to theRestTemplate. This annotation enables theRestTemplateto enable client load balancing function.
4. Load Balancing Test
4.1 Start
Eureka server4.2 Start multiple service provider: service-hello. Here I started 2 services.
1
2java -jar service-hello-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
java -jar service-hello-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=22004.3 Start service consumer: service-hello-consumer
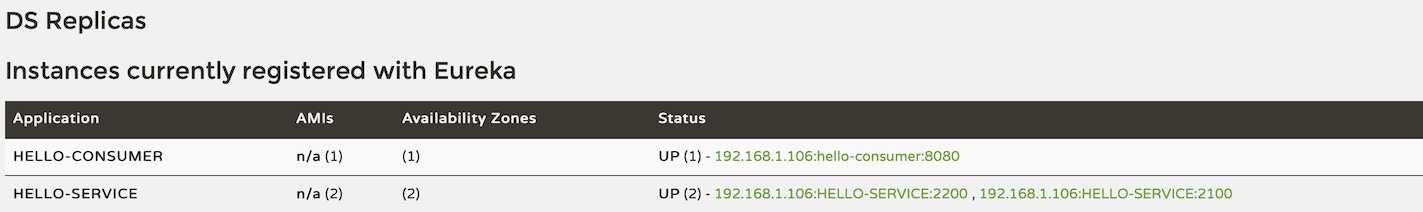
4.4 Open the Eureka server admin page: http://localhost:8761, we can see that two
HELLO-SERVICEservices and oneHELLO-CONSUMERservice have been registered.![]()
4.5 Visit
Hello-Consumer: http://localhost:8080/hello and refresh it multiple times. We can see the following two outputs appear alternately:![]()
![]()
It shows that `hello-consumer` is accessing two service instances of `HELLO-SERVICE` alternately, which means that our load balancing test is successful.
Ribbon’s load balancing strategy
Ribbon itself provides the following load balancing strategies:
- RoundRobinRule: Round robin policy.
Ribbonselects the server in round robin manner. This is the default value. So the two services started in the example will be cyclically accessed; - RandomRule: Random selection, which means that
Ribbonwill randomly select one from the server list to access randomly; - BestAvailableRule: The maximum availability policy. After filtering out the failed server, select the one with the lowest number of concurrent requests;
- WeightedResponseTimeRule: With a weighted polling strategy. The response time of each server is weighted, and then the corresponding server is obtained by polling;
- AvailabilityFilteringRule: Available filtering strategy. First filter out some service instances that have failed or concurrent requests are larger than the threshold, and then select one from the filtered instance list in a linear polling manner;
- ZoneAvoidanceRule: Zone-aware strategy. First use the primary filter (zone loader, select the optimal zone) to filter all instances and return the filtered instance list. Use the filters in the secondary filter condition list to perform on the results of the primary filter. Determine the minimum number of filters (default 1) and the minimum percentage of filtering (default 0), and finally use
RoundRobinRule(polling method) to select a server instance from the server that meets the conditions.
We can implement our own load balancing strategy by inheriting
ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule.
Check out the source code here: Ribbon demo