Eureka is a Netflix open source product that provides service registration and discovery. It provides a complete implementation of Service Registry and Service Discovery. It is also one of the most important and core components of Spring Cloud.
Service Center
The service center is also called the registration center, which manages various service functions including service registration, discovery, fusing, load balancing, and downgrading. So how does it makes service call easier? Let’s see an example.
Without service center, we have service A calls service B, and service B calls service C.

With service center, the service calls have two steps. In the first step, service A first requests the service B from the service center, and then service B requests the service C from the service center.
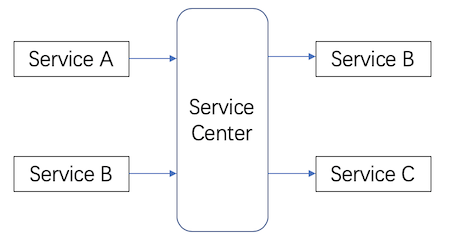
The above examples are just two or three simple calls to each other, but imagine if there are more than 20 and 30 services. With service center you do not need to know the IP address of the service you call, or how many servers it has. Each time simply go directly to the service center and get the services that needs to be call.
Since various services are registered in the service center, many advanced functions can be implemented. For example, having several services providing the same service for load balancing; monitoring the service call success rate for fusing, removing fault points in the service list; monitoring service call time to set different weights for different services, and so on.
Eureka
Spring Cloud encapsulates the Eureka module developed by Netflix to implement service registration and discovery. Eureka uses the C-S design architecture. Eureka Server is the server for the service registration function. It is the service registration center. The other microservices in the system use Eureka Client to connect to Eureka Server and maintain a heartbeat connection. In this way, the system maintenance staff can monitor whether the microservices in the system are running normally through Eureka Server. Some other modules of Spring Cloud (such as Zuul) can use Eureka Server to discover other microservices in the system and execute related logic.
Eureka consists of two components: Eureka Server and Eureka Client. Eureka Server is used as a service registration server. The Eureka Client is a java client that is used to simplify interaction with the server, act as a polling load balancer, and provide failover support for services.
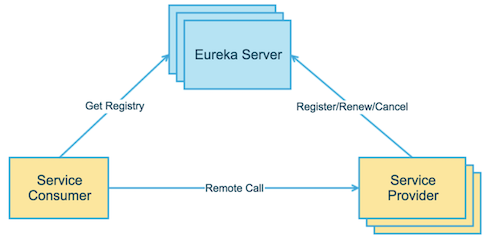
The above diagram briefly describes the basic architecture of Eureka, which consists of 3 roles:
- Eureka Server: Service registration center, responsible for service registration, maintenance and query of service list
- Service Provider: An
Eureka Client, responsible for registering, renewing, and deregistering the services withEureka Server. The main data provided during registration includes service name, machine IP, port number, domain name, etc., so that service consumers can find it - Service Consumer: An
Eureka Client, will also register itself with the services provided byEureka Server. Usually with consumer, it is more to obtain the corresponding service list fromEureka Server, so that it can initiate service calls.
Service Provider and Service Consumer are not a strict concept, often the service consumer is also a service provider, and at the same time, the service provider may also call the services provided by other service providers. Of course, when we build microservices, we still need to adhere to the division between business levels and try to avoid circular dependencies between services.
Example Project
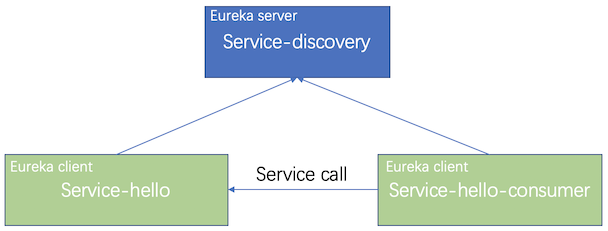
In this example project, I will have 3 modules:
- Service-discovery: As the service registration center and
Eureka server - Service-hello: Service provider and
Eureka client - Service-hello-consumer: Service consumer and
Eureka client![]()
Service-discovery
1. Add dependency
1 | <dependency> |
2. Main class
1 |
|
The key here is adding @EnableEurekaServer, to declare that it is an Eureka server.
3. Configuration file
Configuration is placed under resource/application.properties
1 | server.port=8761 |
eureka.client.register-with-eureka: Whether to register itself with Eureka Server. The default istrue.eureka.client.fetch-registry: Whether to obtain registration information from Eureka Server. The default istrue.eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone: Set the address to interact withEureka Server. Both the query service and the registration service need to rely on this address. The default ishttp://localhost:8761/eureka; multiple addresses can be separated by ‘,’.
4. Start server
Start the server and visit http://localhost:8761, should be able to see the following page:
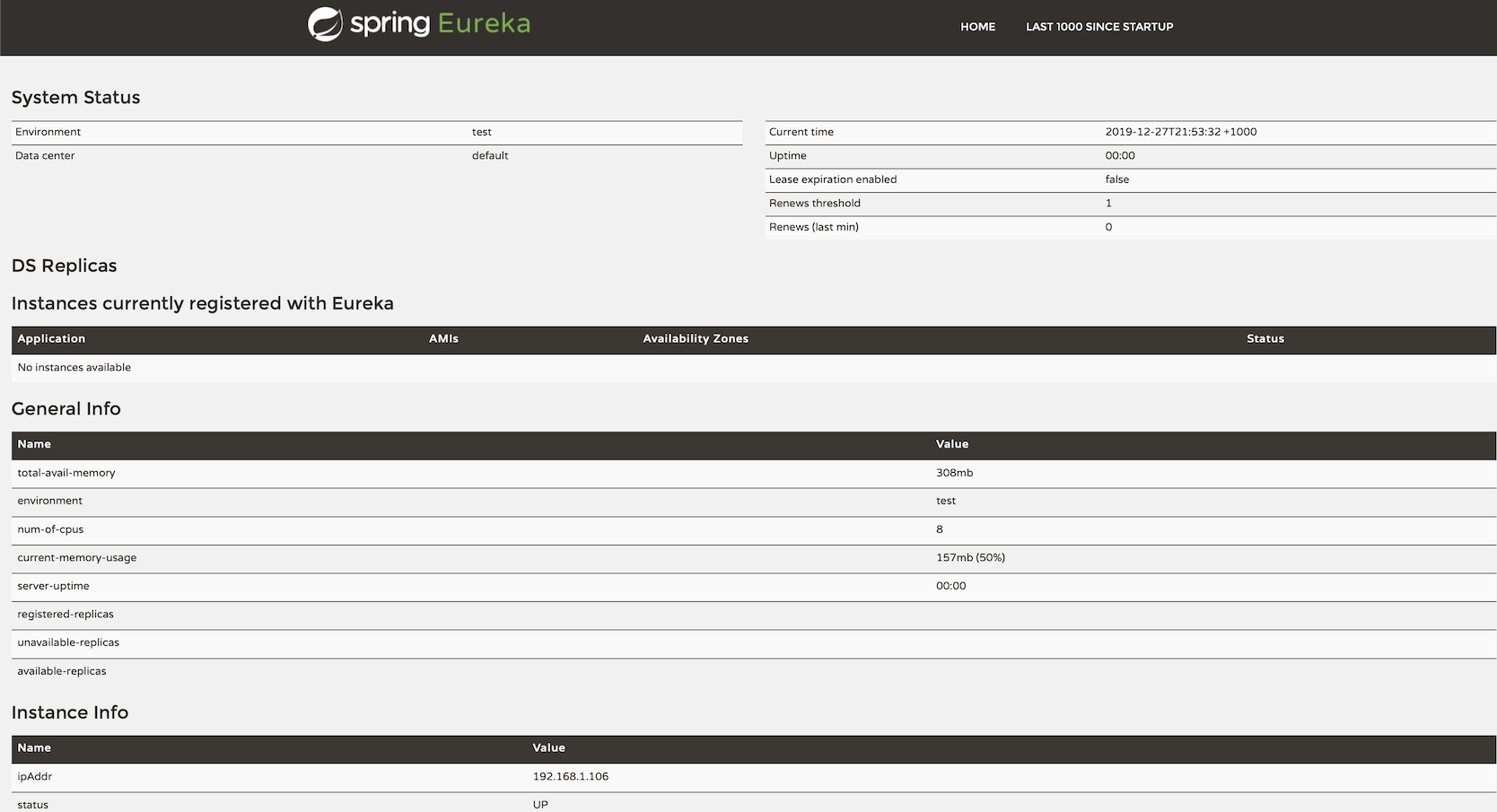
Under Instance currently registered with Eureka section, there is no service instance registered yet.
Service-hello
In this example, we define a simple service. It returns a string Hello, Spring Cloud! When calling the /hello service endpoint.
1. Add dependency
1 | <dependency> |
2. Main class
1 |
|
The difference here with the service-discovery is change the annotation to @EnableDiscoveryClient, to declare that it is an Eureka client.
3. API service
1 |
|
A very simple service provide only /hello endpoint
4. Configuration
1 | server.port=2100 |
Here the spring.application.name must be set. Service consumer find this service by this name. eureka.client.service-url must also be set. It means that we want to register services with those Eureka servers. Here we can declare multiple Eureka servers
5. Start server
After server start-up, should be able to see this console log:
1 | com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient : DiscoveryClient_HELLO-SERVICE/192.168.1.106:HELLO-SERVICE:2100 - registration status: 204 |
Refresh http://localhost:8761:
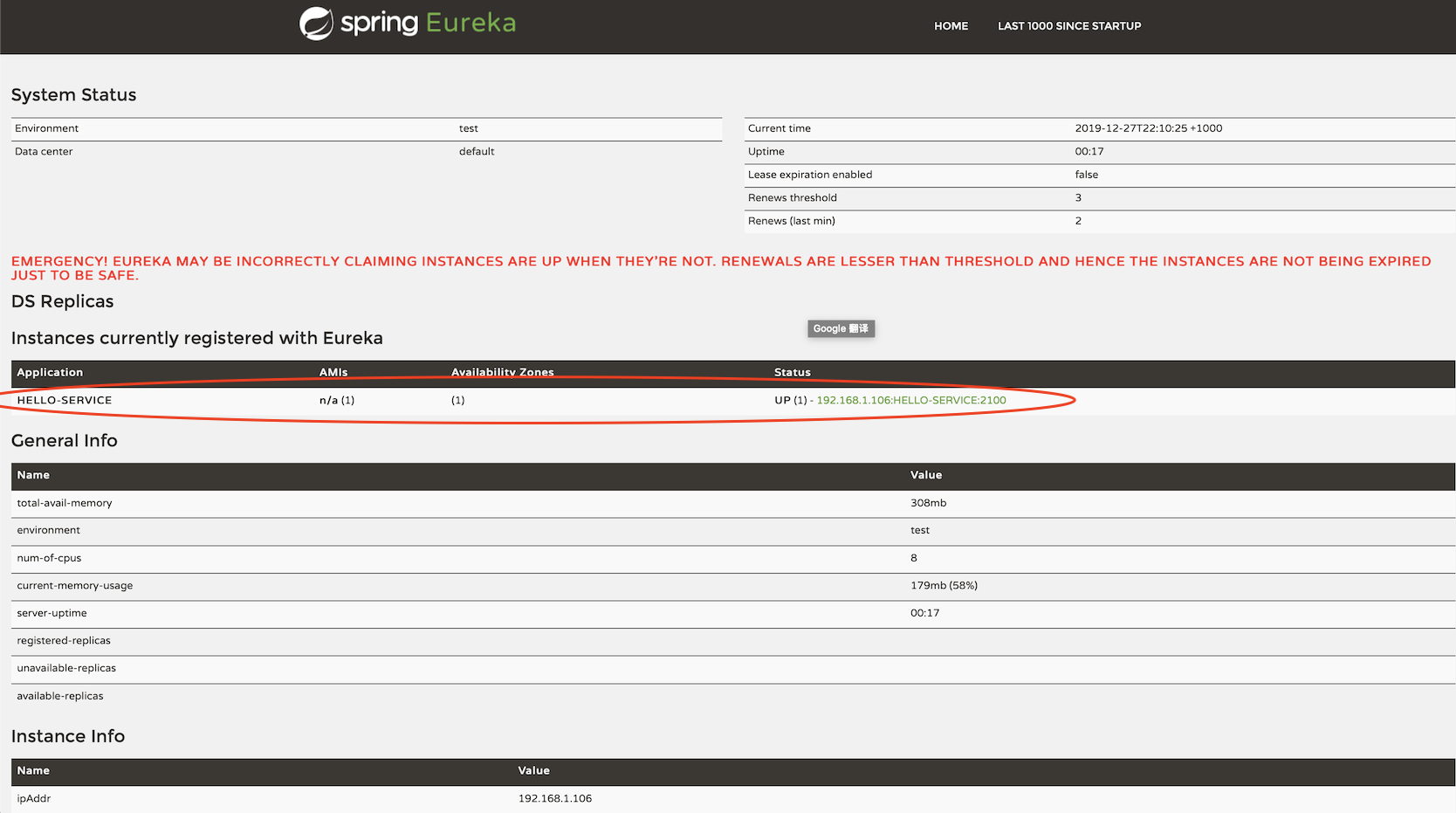
We have successfully registered our service to the Eureka server.
Service-hello-consumer
In the previous sections, a simple Eureka server and client has been built. In order for us to better appreciate the role played by Eureka, let’s build a service consumer that will call the services provided by SERVICE-HELLO.
1. Add dependency
1 | <dependency> |
Same as Service-hello.
2. Main class
1 |
|
Same as Service-hello, annotated with @EnableDiscoveryClient to declare a Eureka client.
3. Service call
1 |
|
The service call is a standard controller. The hello() method will call the SERVICE-HELLO/hello service through the restTemplate and return.
4. Configuration
1 | server.port=8080 |
5. Start server
After server start-up, should also be able to see this console log:
1 | com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient : DiscoveryClient_HELLO-CONSUMER/192.168.1.106:hello-consumer:8080 - registration status: 204 |
Refresh http://localhost:8761:
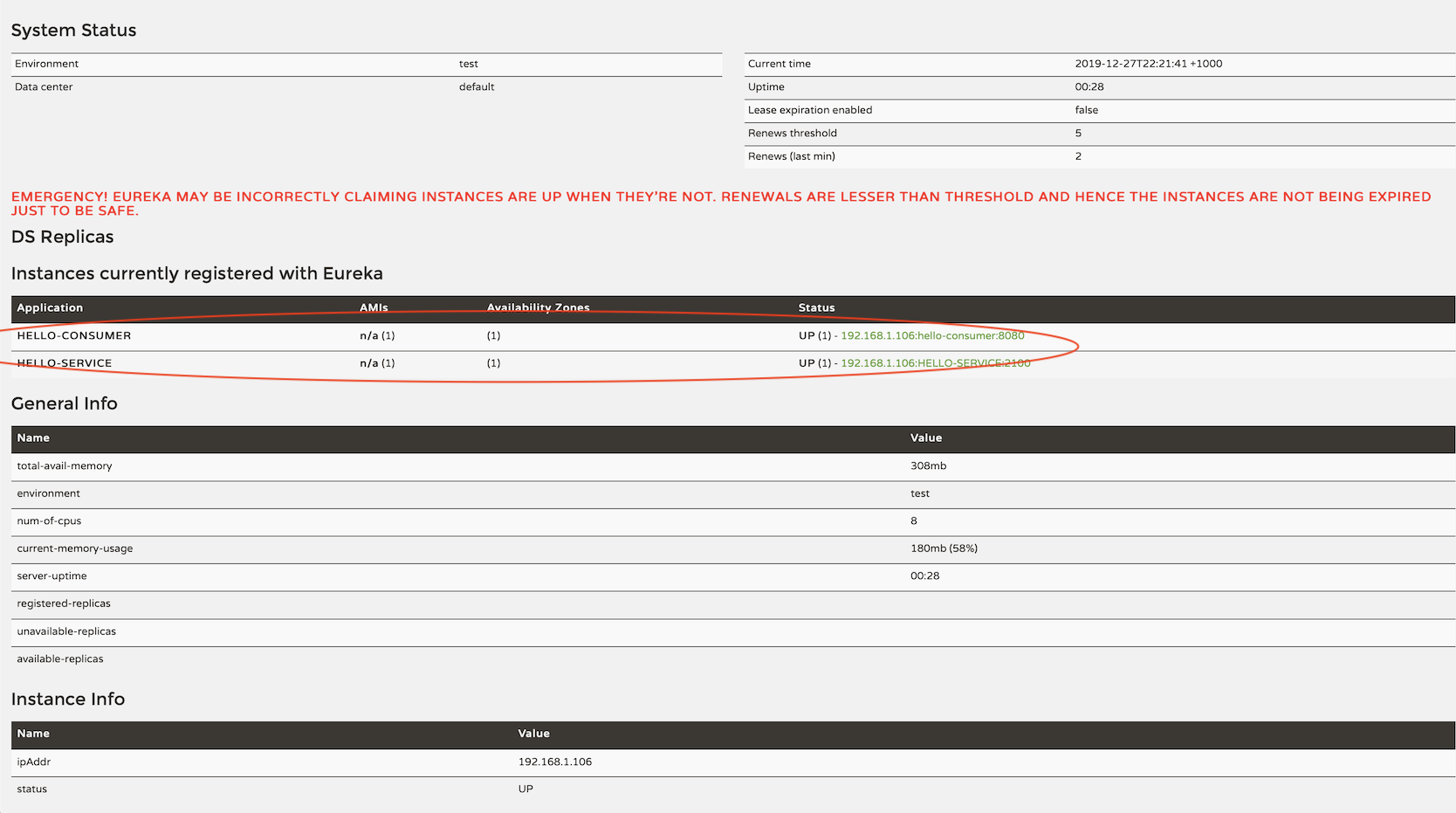
We can see there are 2 services registered.
6. Verify the service call
Visit http://localhost:8080/hello, should see the response:
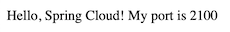
Also the console log of Service-hello should have an output:
1 | INFO 6602 --- [nio-2100-exec-1] s.helloservice.endpoint.HelloEndpoint : /hello, instanceId:192.168.1.106:HELLO-SERVICE:2100, host:192.168.1.106 |
Now we have successfully built our first Spring Cloud Eureka demo.
Check out the source code here: Eureka demo